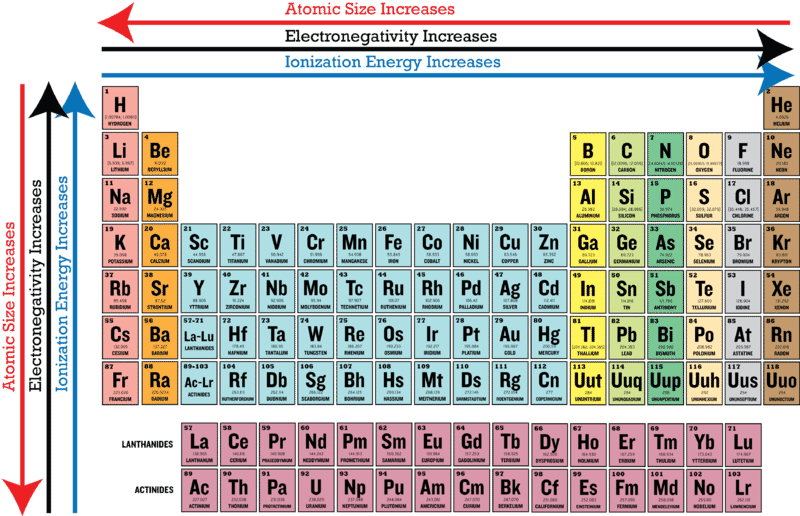
Electronegativity increases left to right and bottom to top. Electronegativity usually rises from left to right.

What Is Electronegativity Trends Chart Periodic Table Chemtalk
There is an increase in the atomic number as we move down the group.
. The trends for electronegativity is that the value increases across the periods rows of the periodic table. By the end of this article you should be able to describe and explain the trends in electron configuration atomic radius electronegativity first ionisation energy and melting and boiling points. As mentioned the electronegativity trend refers to the way electronegativity values trend across the periodic table of the elements.
7 Describe the similarities in group trends on the line graph. Electronegativity tends to decrease down a group of the periodic table. Which group demonstrates the greatest deviation from the other trend shapes.
Describe electronegativity trends in the periodic table. Describe these trends. When we move from left to right in a period of the modern periodic table electronegativity increases.
In this graph we have not shown argon as it does not react with elements to form bonds. You just studied 10 terms. To what volume should you dilute 25 mL of a 120 M H2SO4 solution to obtain a 0170 M H2SO4 solution A sample of metal has a mass of 1525 g and a volume of 725 mL.
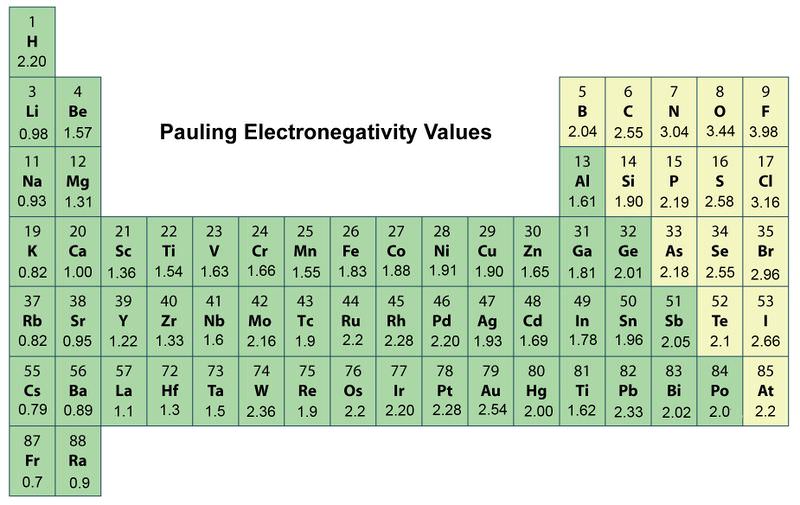
Different elements have different electronegativities based on a number of factors such as size and number of protons neutrons and electrons. Fluorine is the most electronegative element. Trends in electronegativity across a period.
Describe electronegativity trends in the periodic table It increases left to. There are several different ways of measuring it the most common being the Pauling scale. Electrostatic theory explains the trend in electronegativity in the Periodic Table in the Periodic Table both across a period and down a group.
The ability of an atom to attract electrons to itself in a chemical bond is called electronegativity. It sees a decreasing trend when you move down a group. For example the electronegativity trend across period 3 in the periodic table is depicted below.
However there are exceptions to it at times. 6 Describe the 3-D periodic table bar chart of electronegativity values. The electronegativity also increases up a group column of the periodic table.
Electronegativity is the ability of an atom to pull electrons towards it. Describe the trends in atomic radii by checking the correct box. Ionization energy and electronegativity show similar trends in the periodic table.
Periodic Table Trends. What is the significance of the similarity of these trends. Periodic table even though there are more protons in the elements at the bottom of the column.
8 Evaluate the usefulness of a 3-D graph versus a line graph to compare values and analyze trends. Check all that apply. Use the periodic table to determine which elements are likely to have a larger atomic radius than silicon Si.
As you go across the elements in a period each element has an increased effective nuclear charge or Z eff attracting its outer shell electrons. Lithium 10 and Francium 07 in Group I. Electronegativity generally increases from left to right across a period and decreases down a column in the periodic table.
View Chapter 6 Chemistry Testpdf from CHE 107 at Arizona State University. Electronegativity is a measure of the tendency of an atom to attract a bonding pair of electrons. What best describes the trends in electronegativity on the periodic table.
Electronegativity values generally increase from left to right across the periodic table. Describe electronegativity and explain the trend of electronegativity in the Periodic Table. In the periods the electronegativity increases from left to right because the number of electrons in the valence shell increases so the attraction of other electrons increases to complete the valence shell and reach a stable state.
It is often viewed on an. Atomic radii from the left to right across a period tend to. As we move across a period from left to right the nuclear charge increases and the atomic size decreases therefore the value of electronegativity increases across a period in the modern periodic table.
We can see this with the help of a graph showing the trend in electronegativity in period 3 from sodium to chlorine. Metals tend to have lower electronegativities than nonmetals. Electronegativity is a measure of the ability of an atom to attract the electrons when the atom is part of a compound.
Lithium 10 and Fluorine 40 in period 2. Effective nuclear charge is the positive charge that. Electronegativity is defined as an atoms ability to attract electrons towards it in a chemical bond.
Fluorine the most electronegative element is assigned a value of 40 and values range down to caesium and francium which are the least electronegative at 07. In general electronegativity decreases as you move down a group in the periodic table this correlates. When moving from left to right across the periodic table electronegativity increases with the exception being the noble gases.
The trend as you move from left to right across a period in the Periodic Table the electronegativity increases due to the stronger attraction that the atoms obtain as the nuclear charge increases. After that well explore periodic trends as you move down a group in the periodic table. The overall trend for electronegativity in the periodic table is diagonal from the lower left corner to the upper right corner.
The Pauling scale is the most commonly used. Electronegativities generally decrease from top to bottom of a group. It shows how an atom can swiftly form a chemical bond.
Answer Electronegativity increases from left to right within a period and decreases from top to bottom in a group. Atomic Radius Atomic Size-INCREASES from top to bottom-DECREASES from left to right Ionization Energy-DECREASES from top to bottom-INCREASES from left to right Electronegativity Electron Affinity-DECREASES from top to bottom-INCREASES from left to right Metallic Character-INCREASES from top to bottom-DECREASES from left to right. Elements at the top of a column have greater electronegativities than elements at the bottom of a given column.

Periodic Trends Made Easy Chemtalk
0 Comments